Are you looking for a way to maximize your real estate investments and minimize costs? If so, the 1031 exchange code can be a great way for you to save on tax and reinvest in property instead.
Simply put, the 1031 exchange is a real estate investment strategy that many experienced investors apply to switch the focus of their investments or swap their current assets for more lucrative investments.
The 1031 exchange code allows you to avoid paying the capital gains tax if you swap your property for a similar one that has the same or higher value. Instead of using a fraction of the sale proceeds to pay taxes, you can use it for investment purposes.
Sounds great, doesn’t it? Well, things aren’t always as easy as they seem. Many investors use the like-kind exchange strategy to boost their profits and minimize costs, but there are also those who use it in all the wrong ways and end up at a loss.
This article will give you an exact explanation of a 1031 exchange, the rules for doing it, the types of 1031 exchanges that exist, and what you can gain from this form of tax deferment. Keep reading!
Why Should You Use a 1031 Exchange Strategy in Real Estate?
In 2021, real estate prices exceeded decade-long “bubble levels,” creating the opportunity for investors to exchange properties in expensive markets. The latest events have increased the cash flow across the country, and many seasoned investors are taking an opportunity to maximize their investments.
One way to do that is a 1031 exchange.
What Is a 1031 Exchange?
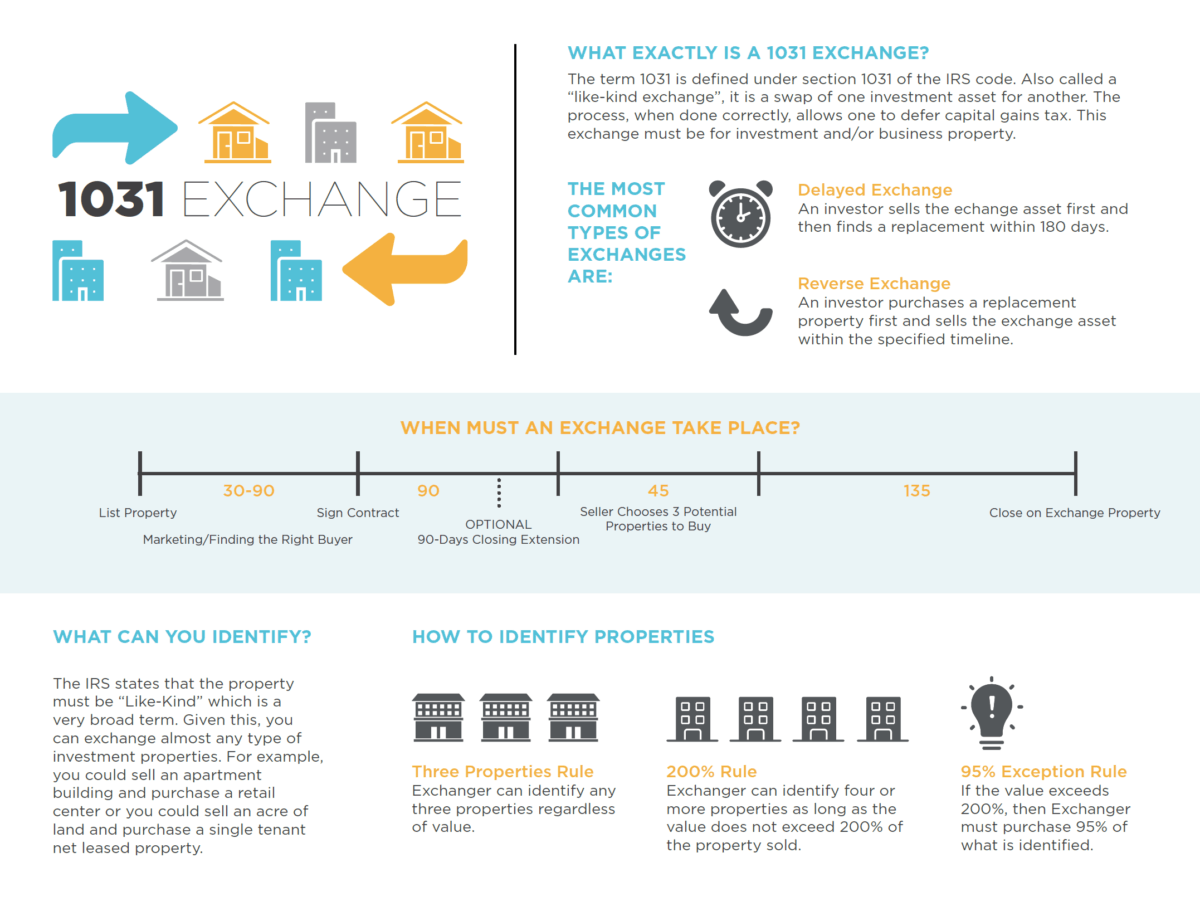
A 1031 exchange (also called a like-kind exchange or Starker exchange) is a strategy for tax deferment that many successful real estate investors use. In general, it involves exchanging one property for another.
This exchange is defined by IRS Code Section 1031, and it allows investors to defer capital gains tax on the sold property if they buy a similar property with the profits from the sale. This strategy is said to create more benefits than just avoiding paying taxes. It also allows investors to change the focus of their investments without being liable for taxes.
This means that if you replace an investment property (like an apartment complex) that requires lots of landlord management for a triple net property that requires little to no landlord management, you’ll be paying fewer taxes and cash flowing more. Or, if you just want to change the location of your real estate (for cash flow or tax reasons), you’ll be able to do this without paying the capital gains tax.
However, there’s a significant drawback to this strategy. It can be hard to find a property of the same or greater value and also find a buyer who is interested in your property in time (hint: a great broker will be able to line up and execute these complex transactions for you).
You’d have to first find an investment property that’s similar to yours (the “upleg,” and then you must find an buyer who is interested in your property (the “downleg”). Because of this, these exchanges usually take a long time unless you work with an experienced team of experts.
After selling your property, you will need to look for additional outside help. In many cases, you will need to find a qualified intermediary (aka a “middleman”) to purchase the second property with the cash from your property. This becomes a third-party exchange and is legally treated as a swap. This is important because you should never be able to access the money directly in order defer the capital gains and avoid getting penalized.
What Are the Benefits of Like-Kind Exchanges?
Typically, when you sell real estate, you need to pay a capital gains tax. This can create more costs for you if you made an investment that requires you to exit.
However, if the price of your real estate increased compared to the price when you bought it, the 1031 strategy helps you profit by obtaining a similar or more expensive property without having to pay a capital gains tax.
You will have to pay taxes eventually (unless you “swap until you drop” and your heirs can cash without ever paying the capital gains), but this enables you to trade without having to pay these taxes right away. This is important if you consider that there are several things you can do in the meantime to profit from real estate.

How to Use a 1031 Exchange Strategy
After deciding to do a 1031 exchange, you need to find a property that has a similar value to the one you’re selling. Keep in mind that this exchange requires that the value of the property you’re obtaining be either the same or higher than your current property.
For example, if you’re selling a $1 million property with a $650,000 loan, you’d have to top the property price along with replacing the loan amount.
There are several different options for completing the actual exchange.
What Are the Types of 1031 Exchanges?
There are a couple of different types of like-kind exchanges:
- Simultaneous. This exchange happens when the closures for the replacement and the relinquished property are done on the same day. However, if the smallest delay happens and the change doesn’t happen simultaneously, taxes will apply.
- This exchange is typically done in two ways:
- The swap, where two parties swap deeds.
- The three-party exchange, where a third party makes the transaction as a qualified intermediary.
- This exchange is typically done in two ways:
- Delayed. This form of exchange is when you first sell your property and acquire the replacement property afterward. In this case, the exchanger is responsible for marketing the real estate, finding a buyer, making a sale, and then hiring a third party to hold the funds and initiate the exchange.
- The third party or intermediary will then initiate the sale of the relinquished property, holding the sales funds for up to 180 days. Here, you’ll have 180 days to find a new, similar property. This gives you 45 days to find the replacement property and 180 days to complete the sale of the investment property.
- This form of a 1031 exchange is the most popular because of the extended time for completing sales, besides the obvious tax deductions.
- Reversed. This type of exchange happens when you purchase replacement real estate by using an exchange accommodation titleholder. However, it requires you to use cash, and a lot of lenders won’t loan money for this type of exchange.
- If you fail to close the sale after 180 days, the exchange will be forfeited. This exchange follows a similar rule as delayed exchanges, with the exception that you have 45 days to identify the relinquished property and 135 days to close the sale on the identified/exchanged property.
- Construction/improvement. This exchange lets you use the exchange equity to make improvements to the property you purchased. In a nutshell, you get to use the money that would be spent on taxes to update the purchased property while it’s being held by the intermediary.
- However, you only have 180 days to do this. For this, you need to meet three criteria: spend the entire exchange equity on upgrades or a down payment in 180 days, find a similar property in 45 days, and find a property that’s either the same or higher value than the one you’re exchanging.
- Also, you need to make the improvements before you can take the title back from the intermediary.
What Are the Rules for the 1031 Exchange?
The main rules of a 1031 exchange include the following:
- Properties need to be like-kind to be exchanged. What are the like-kind properties? This is a broad term that means that properties need to share the same character or nature such as being investment properties.
- Properties can’t be different in quality. This means that, for example, you can’t swap a residence for building equipment. These assets aren’t the same in nature, but you can swap a residence for another residence.
- For example, you’d be allowed to swap an 8-unit apartment for a duplex or a commercial building for a single family rental. You can also swap one for multiple properties and vice versa, as long as they’re similar. Of course, the subject properties need to be located in the US.
- Properties need to be for business or investment purposes. You can’t swap properties for personal use, only for business or investment purposes.
- For example, you can swap your personal residence for a business real estate in the same state or a different one if you’re relocating, but you can’t swap your home for another one or a vacation home.
- Properties need to be of equal value, or the property that you’re exchanging needs to be of more value. If your property is worth X amount of money plus Z amount on the mortgage, you could swap it for one or multiple similar properties, as long as the net worth of those properties is at least the X amount, and you’d have to carry on the Y amount for the mortgage.
- These costs also cover acquisition costs and other relevant fees that go toward funding the transaction.
- You can’t receive a ‘boot.’ This is the profit that’s left if the net worth of your property is higher than the property you’re swapping it for. If there is a price difference, you’ll have to pay taxes on it.
- The exchange needs to be done by the same taxpayer. This means that the same name needs to appear on the title of the property that’s being sold and on the tax return.
- However, there is an exception called Single-Member Limited Liability Company or SMLLC. An SMLLC can sell an original property and the sole member can buy new real estate in the individual’s name.
- For example, if your name is Harry Harrison and you have a company in your name, you can sell the company property and buy a property in your name. You’ll still comply with the 1031 code.
- There’s a 45-day period for you to find the replacement real estate. When it comes to the identification time frame, you have 45 calendar days to find up to three similar properties. This won’t be easy considering the work that goes into identifying a good investment. However, there are strategies such as extending the downleg closing date by 30-60 days so that the 45-day identification clock doesn’t officially start.
- Remember, saving on taxes isn’t your only focus. The real estate also needs to make sense in terms of your investment strategy. Don’t buy an overpriced property and disadvantageous financing just because you want to fulfill your exchange.
- There’s also another rule that is an exception to this rule. You can identify up to four properties whose total value isn’t higher than 200% of your property price.
- You have 180 days to complete the transaction. After you’ve identified a target property, you have 180 days to complete the sale. This means that you need the exchange completed by the 180-day mark or by the due date of the income tax return, extensions included, for the tax year of the sale.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of the 1031 Exchange in Real Estate Investing
If you found a profitable swap that makes sense from a strategic point of view, the 1031 exchange can improve your position significantly. This can mean a great deal if you have a good eye for the market and can predict when a market is about to grow.
However, this can cost you a great deal if you don’t understand how the market landscape changes. Remember, it is the prospect of obtaining real estate that can grow in value that makes this strategy worthwhile. A short-term money-saving strategy can’t make up for the possible losses if you don’t find a profitable swap to begin with.
This is related to another disadvantage, which is the reduced replacement property depreciation basis. If you don’t choose a market with the potential to grow and you’re still responsible for the initial property capital gains, you could be at a significant loss if the replacement property doesn’t end up being profitable.

Tips for a Successful 1031 Exchange in Real Estate Investing
While the biggest advantage of this strategy is that you don’t have to pay capital gains tax, I advise acquiring real estate in the strongest markets. You should swap high-value properties for those with turnkey and cash-flow opportunities to maximize the benefits of tax savings.
This means that you should focus on the properties that:
- Create monthly cash flow (rentals, business office spaces, etc.)
- Are easily manageable (industrial buildings, storage spaces, etc.)
- Provide the most freedom (triple nets, single tenants, etc.)
Real estate investment properties like these provide a lot of opportunity to profit with low maintenance.
1031 Exchange Success Strategies
Play your cards right and you can gross substantial returns. For example, if you sell a $1,500,000 property without the exchange, you’ll pay off a $500,000 mortgage and pay $150,000 in taxes. You’re left with $850,000 to reinvest.
But with this exchange, you’ll do the same without paying the $150,000 in taxes, which will leave you with $1,000,000 to invest. The difference in the cash flow, considering the 10% yearly cash-on-cash return, is going to be $75,000.
Another important advantage of this is that large properties come with greater principal reduction, larger profits, and increased appreciation inflation. To gain these profits:
- Work with an attorney and an intermediary from the get-go to make sure that you’re 100% compliant with the 1031 code.
- Look for a replacement property before initiating the 1031 process. Research the market carefully so you know your other options by the time you put the relinquished property under contract.
- Work with a broker who is specialized in finding a similar property to yours, meaning that they specialize in the exact type of property that you are selling. Work with a good broker who has search systems, databases, and research strategies that will help you find as many similar properties as possible to choose from.
- Don’t wait 45 days to put the identified property under contract. Do that as soon as possible so that you can run all the due diligence before the deadline. This will give you enough time to repeat the process in case you choose to back out.
- Research and understand the purchase and sale agreement with upfront payments beforehand, and go for an offer within the agreement instead of sending a letter of intent. This gives you more time and prevents possible delays.
- Make offers that make sense regardless of the initial price of the real estate. You never know which strategy the seller will use when negotiating. Even if the property is overpriced, they might be willing to significantly reduce the price as long as they believe you have a higher probability of closing since you are in a 1031 exchange.
Typical 1031 Exchange Mistakes That Lead to Failure
Now that you know the strategies for the best 1031 exchange, let’s look at the usual errors to watch out for.
Aside from the obvious, which would be missing deadlines, failing to find replacement properties with potential, and working with less-than-competent brokers and attorneys, there are a couple more things to be wary of:
- Putting all your eggs in one basket. This is another way to say don’t commit to a single property as your only option. What if the deal falls through? Missing the 45-day mark is a big risk with the 1031 code.
- Given that this period includes holidays and weekends, you’re technically left with much less time than you think. Plus, the Treasury Regulation requires that you identify the property prior to the 45-day expiry.
- Receipt Requirements Incompliance. The Treasury Regulations impose receipt requirements under Section 1031.
- If you’re doing an improvement exchange, this process is a bit trickier because you have additional requirements for identifying properties. These properties also have specific receipt requirements.
- Overpaying for replacement properties. If you put yourself in a time squeeze and the seller is aware that it’s urgent for you to find a property, they might hardball negotiate against you. To avoid this, be diligent in finding as many prospective replacement properties as soon as possible.
- Buying solely for the purposes of the 1031 exchange. The 1031 code is a great way to save money on lucrative investments. It’s not a profiting strategy on its own. If you purchase or swap for a less profitable property compared to the one you had, you will be at a loss.
- Rushing through paperwork. There’s a great deal of formality surrounding the 1031 exchange, and failing to comply with all of the requirements can result in paying taxes. Pay attention to numbers, deadlines, expenses, and adjustments, and make sure to handle them with laser precision.
- Not accounting for future taxes. There are still plenty of taxes and obligations to be paid in the future, as with any other real estate investment. Plan and account for them to avoid unfavorable economic consequences and to minimize costs wherever possible.

The 1031 Exchange in Real Estate FAQ
What Are G(6) Restrictions, and How Are They Relevant to the 1031 Exchange in Real Estate?
These restrictions limit taxpayers from obtaining the cash or any other benefits from the exchange. They impose defining this in exchange agreements and also define in which circumstances the exchange will be considered unsuccessful and funds returned to the taxpayer.
These limitations are imposed to make sure that the taxpayer doesn’t hold possession of the funds from the sale but instead trades relinquished for replacement assets. Simply put, these restrictions ensure that you won’t receive money for the sold property to buy the replacement property, which would be a taxable sale. Consider cash out refinancing the upleg property and receive that cash tax-free instead.
Can I Make a Like-Kind Exchange With Anyone I Choose?
No. There are certain limitations to who you can exchange properties with, and there are exceptions to these rules as well. You can’t swap like-kind real estate with ‘related’ taxpayers to avoid abuse. But you can make this exchange with family members or business partners.
The requirement for this is that the common owner owns more than 50% of the partnership, whether it’s a family member or corporation.
What Are the Like-Kind Properties?
Real estate should meet the “like-kind” requirements for as long as it’s treated for business or commercial use. In this sense, different types of properties can be considered to be like-kind if they’re not intended for personal use.
How Does the 1031 Exchange Relate to Reinvestment Goals?
If you trade properties for those that are equal to or higher in value, you could avoid paying state tax, healthcare tax, recapture of depreciation, and capital gains tax. But you need to use the proceeds from the transaction for investment purposes.
Also, you need to take a debt that is either equal to or higher than the amount of debt paid off after the relinquished property sale.
Where Can I Find the Paperwork for the Like-Kind Exchange?
Your qualified intermediary will provide you with all the necessary information, documents, and requirements for the exchange. In general, the following paperwork is common across different states in the US:
- An Exchange Agreement,
- Assignments of the taxpayer’s rights in the agreement and sale,
- Seller and buyer notices,
- Replacement properties forms,
- And others.
Who Are the Qualified Intermediaries, and Why do I Need Them?
A qualified intermediary (QI) is an entity (a person or a company) who facilitates the 1031 tax-deferred exchange. A good QI needs to meet the following requirements:
- Isn’t the taxpayer
- Isn’t a disqualified person
- Signs an agreement with you to acquire the relinquished property and transfer it to the buyer and then acquires the replacement asset and transfers it over to the taxpayer (you)
- Doesn’t give or lend money to the taxpayer (you) or otherwise offer benefits to the taxpayer
As you can see, the QIs have a role to make the whole 1031 exchange process easier, faster, and legally more secure. Because the qualified intermediary industry currently isn’t regulated nationwide, you should be careful and find one with the highest level of expertise.
Final Thoughts
The 1031 exchange or like-kind exchange is a great strategy to boost an already profitable buy. Remember, this form of tax deferment isn’t made for you to profit. It is intended to support investment in business or commercial assets.
I don’t recommend choosing the like-kind exchange solely for the purpose of not having to pay the capital gains tax. Remember, the property that you will purchase comes with future costs, and this is where being short-sighted can cost you a lot.
The prospect of saving hundreds of thousands of dollars can keep you from seeing that the replacement property may not be the best choice or that it will cost you a lot in the long run. This is why it’s important to focus on the investment value within the frames of your investment goals and best strategies.
If you choose to use this strategy, make sure to be quick and diligent with identifying the potential replacement properties. Any delays could be detrimental to the process if you miss the 45-day identification period, and you could end up having to pay the capital gains tax after all.
Like any other investment strategy, the like-kind exchange will only be worthwhile if the replacement property has the potential to bring profit. Aside from that, make sure to work with a highly experienced qualified intermediary who can make the whole process a lot easier and safer. Here is a book that I highly recommend all investors and brokers to read in regards to properly performing a 1031 Exchange.
Before you go, check out my list sharing the 7 Essential Books for Real Estate Investors